Turkey’s geography is a fascinating blend of diverse landscapes, climates, and regions that offer unique experiences to travelers and locals alike. From the towering mountains of the east to the fertile plains of the west, and the stunning coastlines along the Mediterranean and Aegean seas, Turkey’s regions each boast their own charm and cultural identity.
Introduction to Turkey’s Geography
Located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, Turkey is uniquely positioned as a transcontinental country. This location contributes to its strategic importance and rich historical background. The country spans an area of approximately 783,356 square kilometers, with diverse topography including mountain ranges, plateaus, river valleys, and coastal plains.
Key Geographic Features of Turkey
- The Taurus Mountains
- The Pontic Mountains
- The Anatolian Plateau
- The Marmara Region
- The Aegean and Mediterranean Coasts
- The Central Anatolian Steppe
Major Regions of Turkey
Turkey is traditionally divided into seven geographical regions, each with distinct climates, cultural practices, and natural landscapes.
1. Marmara Region
- Location: Northwestern Turkey, including Istanbul and Bursa
- Features: Urban centers, industrial zones, and fertile lands
- Climate: Transitional between Mediterranean and oceanic
2. Aegean Region
- Location: Western coast along the Aegean Sea
- Features: Olive groves, ancient ruins, and resort towns
- Climate: Mediterranean, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters
3. Mediterranean Region
- Location: Southern coast along the Mediterranean Sea
- Features: Tourist hotspots like Antalya and Alanya, citrus groves
- Climate: Mediterranean, ideal for tourism and agriculture
4. Central Anatolia Region
- Location: Inland plateau surrounded by mountain ranges
- Features: Steppe landscape, historic cities like Ankara and Konya
- Climate: Continental, with cold winters and hot summers
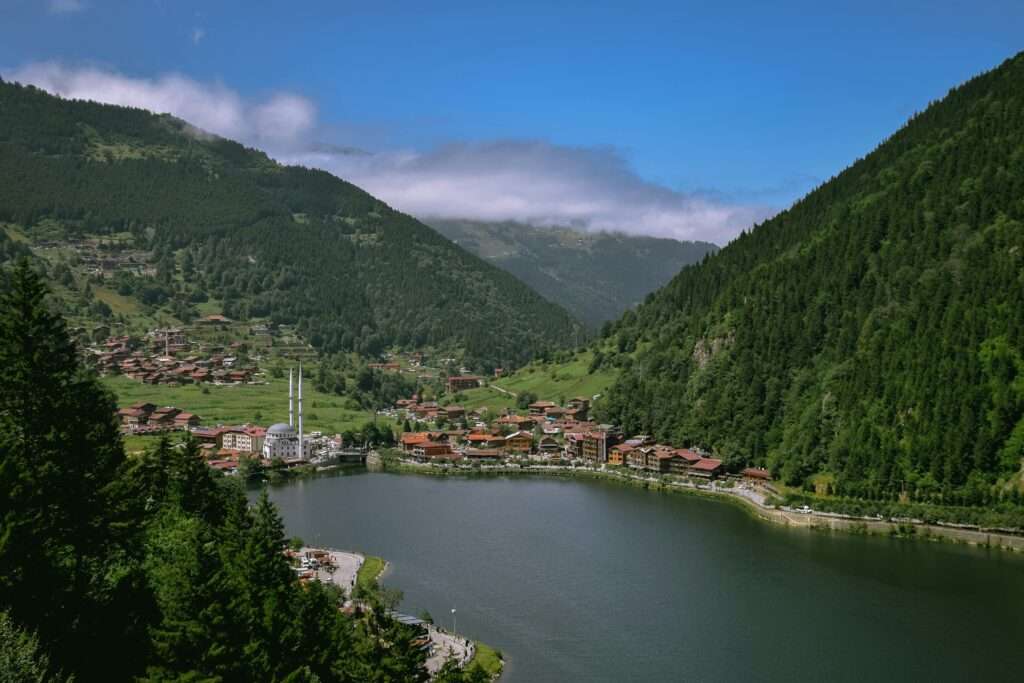
5. Black Sea Region
- Location: Northern coast along the Black Sea
- Features: Dense forests, tea plantations, and rugged coastline
- Climate: Oceanic, with high precipitation year-round

6. Eastern Anatolia Region
- Location: Eastern Turkey, mountainous and less populated
- Features: High altitudes, harsh winters, and unique cultural heritage
- Climate: Harsh continental climate
7. Southeastern Anatolia Region
- Location: Southeastern Turkey, bordering Syria and Iraq
- Features: Fertile plains, cultural diversity, and historic sites
- Climate: Semi-arid, with hot summers and mild winters
How Geography Influences Turkish Culture and Economy
The geographical diversity shapes local economies — coastal areas thrive on tourism and agriculture, while eastern regions focus more on livestock and traditional crafts. Similarly, cultural practices and cuisine vary widely across regions, offering travelers an authentic and varied experience.